A Determined and Differentiated Cells Are Different Explain These Differences
Occurs prior to differentiation gives an operational definition commits cell to a subset of cell types I think it is when gene expression is changed but final morphology is not achieved difference between determination and differentiation. 61 is an overview of the interactions of the small molecules with various cell types.
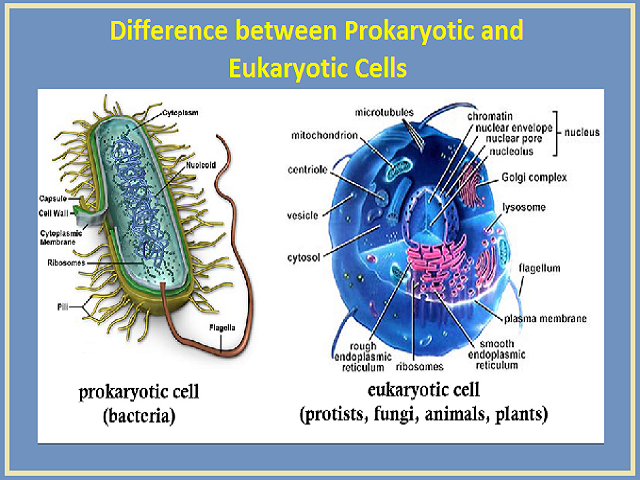
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Morphology but the same DNA with a different set of genes expressed.
. Those trillions of cells are not all the same though. However two types of cells in an adult organism may have clearly different phenotypes eg. Cell Differentiation Mechanism.
Differentiation results from differential gene. Terminally differentiated cells are another important target for small molecules in in vivo tissue regeneration. Stem cells grow and self-renew in the same place of the body where they were derived.
Through cell differentiation tissues as different as brain tissue and muscle are formed from the same single cell. To explain this it would seem that there must be some. Once a cell becomes differentiated it only.
Determination occurs when the fate of a cell is determined differentiation is when the cell actually becomes the cell it is. A mature well-differentiated cell usually has a very specific role to play with characteristics. Differentiated cells in a plant become grouped into tissues and the eventually roots stems and leaves kind of how differentiation occurs in animals.
Place of Action Stem Cells. The regions genes that are expressed determine the type of cell that will be created. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types.
Differentiation is induced by specific stimuli. In plants an undifferentiated plant cell can change to meet a need in the plant. Differentiation follows determination as the cell elaborates a cell-specific developmental program.
When cells express specific genes that characterise a certain type of cell we say that a cell has become differentiated. Transcription factors are key to the cell differentiation process. That means that just one cell a fertilized egg is able to become the trillions of cells that make up your body just by dividing.
But once differentiated or established these cells are stimulus independent. While there are different hormones involved all plants also develop from a single cell. When a cell differentiates becomes more specialized it may undertake major changes in its size shape metabolic activity and overall function.
A muscle cell needs to contract while a sperm cell needs to swim to the egg. The multipotent hematopoietic stem cells give rise to many different cell types including the cells of the immune system and red blood cells. Undifferentiated Cells are the cells that did not receive any particular roles ie.
This synthesis is catalyzed by proteins called enzymes. While the different types of cells that are formed contain the same DNA its the expression of different genes that results in different types of cells. Humans have different types of cells which have different functions.
The key difference between cellular differentiation and cell division is that cellular differentiation is the process of forming a variety of cell types that have specific functions while cell division is the process of splitting a parent cell into two daughter cells. In the following sections we will describe the in vitro and in vivo uses of small molecules to regulate the fate of various cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem.
The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique function in the body whereas undifferentiated cells are responsible for replenishing old injured or dead cells. Differentiation is Different In order for cells to become whole organisms they must divide and differentiate. Cell differentiation allows a cell to specialize to achieve a specific function Multicellular organisms eg.
The biochemical basis of cell differentiation is the synthesis by the cell of a particular set of proteins carbohydrates and lipids. Differentiated cells in addition possess a variety of proteins. Investigate how cell differentiation and gene expression work the.
Differentiated cells are morphologically distinct from their stem cells by size shape metabolic activity membrane potential and responsiveness to signals. Differentiation results in the presence of cell types that have clear-cut identities such as muscle cells nerve cells and skin cells. While the plant lifecycle sometimes seems alien and complex the process of cell differentiation is very similar.
The reason for the different phenotypes reflects their different DNA. Cell differentiation is the process that gives generic cells a specialized purpose through a process known as gene expression. Each enzyme in turn is synthesized in accordance with a particular gene or sequence of nucleotides in the DNA of the cell.
So these cells only have one role for each. Determination implies a stable change - the fate of determined cells does not change. Hence cell differentiation can be ascribed to the pattern of gene expression which is to say that in each differentiating cell type different genes are differently expressed.
When the cells from a poorly differentiated tumour travel to a lymph node or other part of the body additional tests such as immunohistochemistry may be required to. Cells divide all the time. Differentiation is accomplished by morphological difference of that fated or determined cell.
Muscle cell cannot work as a bone cell. Since all cells in the body beginning with the fertilized egg contain the same. Differentiation is the process that shapes the immature cells destiny determines the cells distinct role and results in specific characteristics tailored to the adult cells purpose.
Moderately differentiated The cells in these cancers are clearly abnormal looking but they still share some features with the surrounding normal cells. Poorly differentiated These cancers look very abnormal. 2 A skin cell is unlike a blood cell for example.
Look at the figure different shapes or morphology of various types of cells in our body. Differentiated Cells are the cells that is specialized after receiving an electrical signal from the body. Cell differentiation is the process by which cells specialize to achieve their required functions.
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one Usually the cell changes to a more specialized type. Given two multi-cellular species with obviously different phenotypes. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
Differentiation occurs in both.
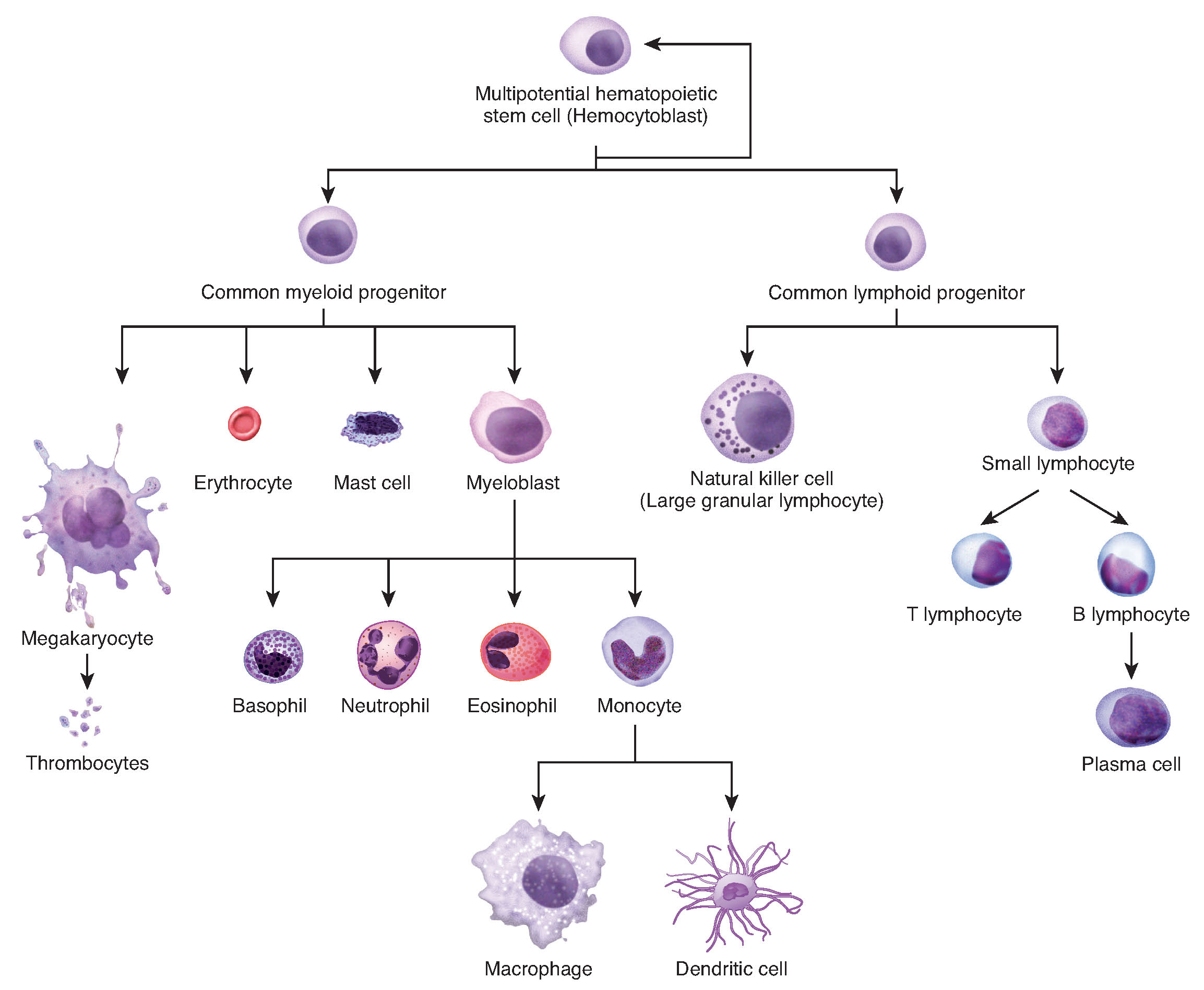
Cellular Differentiation Anatomy And Physiology
What Is The Difference Between Cell Determination And Cell Differentiation Pediaa Com
What Is The Difference Between Cell Determination And Cell Differentiation Pediaa Com
What Is The Difference Between Cell Determination And Cell Differentiation Pediaa Com
No comments for "A Determined and Differentiated Cells Are Different Explain These Differences"
Post a Comment